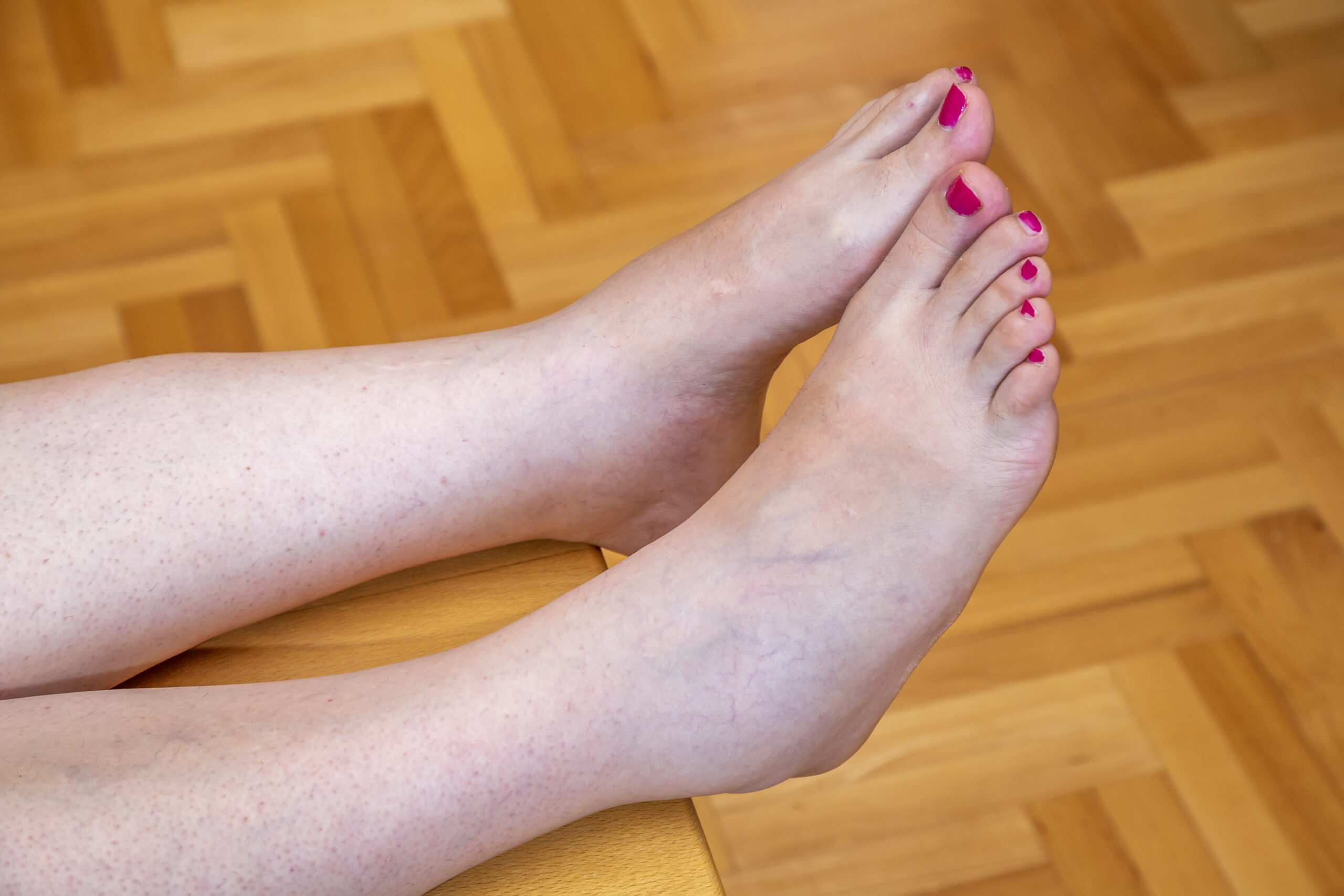
Edema, or swelling, in either the upper extremity or lower extremity, is caused by fluid accumulation within the tissues, and between the cells of the tissues. Normally, excess fluid can be transported from the cells into the transport pipes to be carried out of the extremities. These transport pipes are either the veins or lymphatics. Any overloading, insufficiency of transport, or obstruction of these pipes will cause pooling of fluid in the tissues. There are essentially four main causes of swelling in the legs.
Venous Disease
Fluid is transported into the veins of the legs from surrounding tissues, then moved out of the legs back to the heart very quickly. Most veins are branches of the main deep or superficial veins which have valves to control movement upward, out of the legs against gravity. If there is an obstruction to the main veins because of a blood clot or compression of the vein, the pressure builds and limits the fluid leaving the tissues. If the valves of the main veins do not work, then there is back pressure, called venous hypertension, again limiting the transport of fluid from the tissues.
The swelling may be described as brawny with the distribution at the calf and ankles with the feet having a little edema. Slow development of thin skin and hyperpigmentation at the calf or described gaiter area. This is also the most common area where venous ulcers develop. Patients who usually have unilateral swelling with the other limb having minimal venous disease.
Most of the time after a blood clot, the veins over time may clear themselves. If a person is found to have incompetent or non-functional valves, there are treatments to close the bad veins to allow the normal ones to work better for fluid transport.
Lymphedema
Most people have heard of lymph nodes, which can be a place for metastatic cancer or infection. Cancer cells and fluid get to the lymph nodes by way of lymphatic channels or tubes. Lymphedema can be seen from a young age or develop later in life. This can be caused by congenital abnormalities within the routes of the lymphatics or obstruction from infections, inflammation, or trauma. If the lymph nodes are removed during surgery or the channels are closed from disease or disrupted at the time of surgery, this will reduce the slow removal of fluid from the tissues.
The swelling can be described as spongy with more thickened skin changes, rarely with pain, and usually unilateral which includes the feet. Some people experience a dull aching discomfort. There is no good way to treat or reverse disease of the lymphatic. Some physical therapists are certified in lymphatic treatments and along with compression is the main therapy.
Lipedema
Lipedema is a chronic medical condition characterized by a symmetric buildup of adipose tissue (fat) in the legs and arms. A common but under-recognized disorder, Lipedema may cause pain, swelling, and easy bruising.
-Lipedema Foundation
The cause of this is unknown. Few treatments are advised routinely as successful. It is much more common in females and persons with a BMI greater than 35. It is not caused by obesity. It can often be confused with a diagnosis of lymphedema. Limb compression, exercise, good, diet, and liposuction have all been used for patients with lipedema. The Lipedema Foundation has good information for further education.
Systemic Causes
Systemic causes can be secondary to the involvement of several organ systems. This can involve any disease entity that will affect the blood flow to the kidney, and therefore the removal of fluid from the body. Many fall under the category of causing Secondary Aldosteronism. Systemic causes include
Heart failure
Liver failure, including cirrhosis
Kidney failure
Malnutrition
Pregnancy
Inflammatory processes
This type of edema is usually seen in the bilateral legs with little pain. Pitting, meaning when you press on the skin, an indention will remain, is common. Improvement of the edema is dependent on the treatment of the underlying cause usually by medicines. In the meantime, compression therapy is the main treatment of the edema.
Recommended Compression Therapy
For everyday use, a 15 to 20 mmHg knee-high compression stocking could be valuable. These are recommended for anyone working in retail, food, service, construction, nursing and healthcare, or anyone sitting or standing for long periods. This is a good strength for travel also. If you or your family members should have inflammation of the skin with swelling, or edema, then 20 to 30 mmHg may be of more benefit.
Do Any Tests Help Diagnose The Cause?
A noninvasive ultrasound examination may be scheduled before or after the evaluation and will help differentiate between the causative entities. Blood testing may be ordered after the initial consultation.