What is Revascularization?
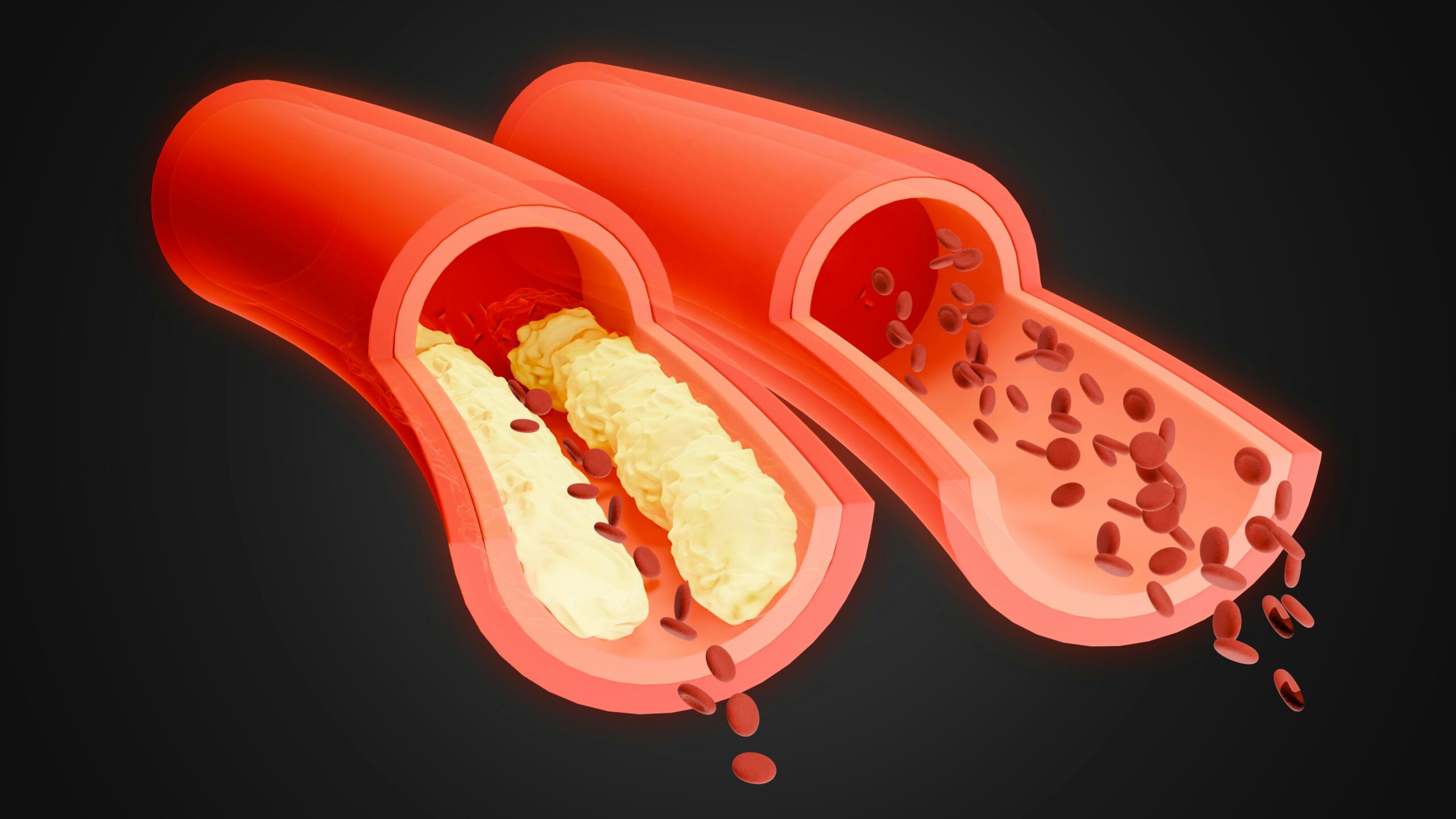
Revascularization is a medical procedure designed to restore blood flow to areas of the body where circulation has been compromised. This usually occurs when arteries become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque, a condition known as atherosclerosis. At Snake River Vascular Surgery we know that revascularization is a crucial treatment for individuals with cardiovascular conditions, such as coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and cerebrovascular disease, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other serious health complications if left untreated.
Why is Revascularization Necessary?
The circulatory system delivers oxygen and nutrients to organs and tissues throughout the body. When blood vessels become blocked, it restricts this essential flow, leading to symptoms like pain, fatigue, and, in more severe cases, tissue damage or organ failure. Revascularization restores normal circulation, helping to alleviate symptoms, prevent damage, and improve overall quality of life.
Common conditions that may require revascularization include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked, causing chest pain (angina) or increasing the risk of heart attacks.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): A condition where blood flow to the limbs is reduced due to blocked arteries, causing pain and difficulty walking.
- Cerebrovascular Disease: Blockages in the arteries supplying blood to the brain can increase the risk of stroke or transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes).
Types of Revascularization Procedures
There are different types of revascularization procedures, depending on the location and severity of the blockage, as well as the patient’s overall health. Here are some of the most common techniques used to restore blood flow:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting, or CABG, is one of the most well-known revascularization procedures used to treat coronary artery disease. During this surgery, a healthy blood vessel—usually taken from the leg, arm, or chest—is grafted onto the blocked coronary artery to create a new pathway for blood to flow to the heart. CABG is often recommended for patients with multiple or severe blockages that cannot be treated effectively with less invasive methods.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open narrowed arteries. A small balloon is inserted into the blocked artery and then inflated, pushing the plaque against the artery walls and widening the vessel. Often, a stent (a small wire mesh tube) is placed in the artery to keep it open and maintain blood flow. Angioplasty and stenting are commonly used to treat both coronary and peripheral artery disease.
- Endarterectomy: Endarterectomy involves surgically removing plaque from the inside of a blocked artery. This procedure is frequently performed on the carotid arteries (the vessels that supply blood to the brain) to reduce the risk of stroke. By removing the blockage, the blood can flow freely, decreasing the likelihood of future cardiovascular events.
- Laser Revascularization: In some cases, a laser is used to dissolve blockages in the arteries. Laser revascularization is less common but may be used in specific situations where traditional methods are not feasible.
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): Also known as coronary angioplasty, PCI is performed by inserting a catheter with a small balloon attached into the narrowed artery. Once the balloon is inflated, it widens the artery to restore blood flow. This procedure is often followed by stent placement to prevent re-narrowing of the artery.
Benefits of Revascularization
The primary goal of revascularization is to restore adequate blood flow to affected areas, relieving symptoms and improving organ function. Key benefits include:
- Symptom Relief: Revascularization can significantly reduce symptoms such as chest pain (angina), leg pain, and shortness of breath, allowing individuals to engage in daily activities with less discomfort.
- Prevention of Heart Attacks and Strokes: By restoring blood flow, revascularization reduces the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other serious cardiovascular events.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients who undergo successful revascularization often experience improved physical function, mobility, and a greater sense of well-being.
- Tissue and Organ Protection: Restoring blood flow to blocked areas helps prevent damage to tissues and organs, such as the heart, brain, or limbs, which could otherwise result in permanent impairment or loss of function.
If you think you may benefit from revascularization, please call us at Snake River Vascular Surgery to see how we can help you!